Linked List Problems
-
Question 1. Reverse Linked List
Easy
Solution
Given the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.

class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
def reverse_list(head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
curr = head
prev = None
while curr:
next_node = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next_node
return prev
assert reverse_list([1,2,3,4,5]) == [5,4,3,2,1], "Test case 1 failed"
assert reverse_list([1,2]) == [2,1], "Test case 2 failed"
assert reverse_list([]) == [], "Test case 3 failed"
print("Test cases passed :)")
-
Question 2. Merge Two Sorted Lists
Easy
Solution

You are given the heads of two sorted linked lists list1 and list2.
Merge the two lists into one sorted list. The list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Return the head of the merged linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
def merge_two_lists(l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if l1 is None:
return l2
if l2 is None:
return l1
if l1.val < l2.val:
l1.next = merge_two_lists(l1.next, l2)
return l1
else:
l2.next = merge_two_lists(l1, l2.next)
return l2
assert merge_two_lists([1,2,4], [1,3,4]) == [1,1,2,3,4,4], "Test case 1 failed"
assert merge_two_lists([], []) == [], "Test case 2 failed"
assert merge_two_lists([], [0]) == [0], "Test case 3 failed"
print("Test cases passed :)")
Question 3. Reorder List
Medium
Solution
You are given the head of a singly linked-list. The list can be represented as:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln Reorder the list to be on the following form:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → … You may not modify the values in the list’s nodes. Only nodes themselves may be changed.

class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
def reorder_list(head: ListNode) -> None:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
# Find the middle of the list
slow = fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# Reverse the second half of the list
prev, curr = None, slow
while curr:
curr.next, prev, curr = prev, curr, curr.next
# Merge the two halves
first, second = head, prev
while second.next:
first.next, first = second, first.next
second.next, second = first, second.next
return head
assert reorder_list([1,2,3,4]) == [1,4,2,3], "Test case 1 failed"
assert reorder_list([1,2,3,4,5]) == [1,5,2,4,3], "Test case 2 failed"
assert reorder_list([1,2]) == [1,2], "Test case 3 failed"
print("Test cases passed :)")
Question 4. Linked List Cycle
Easy
Solution
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail’s next pointer is connected to. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.

class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
def has_cycle(head: ListNode) -> bool:
if not head or not head.next:
return False
slow = fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast:
return True
return False
node1 = ListNode(3)
node2 = ListNode(2)
node3 = ListNode(0)
node4 = ListNode(-4)
node1.next = node2
node2.next = node3
node3.next = node4
node4.next = node2
assert has_cycle(node1) == True, "Test case 1 failed"
node1 = ListNode(1)
node2 = ListNode(2)
node1.next = node2
node2.next = node1
assert has_cycle(node1) == True, "Test case 2 failed"
node1 = ListNode(1)
assert has_cycle(node1) == False, "Test case 3 failed"
Question 5. Remove Nth Node From End of List
Medium
Solution
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
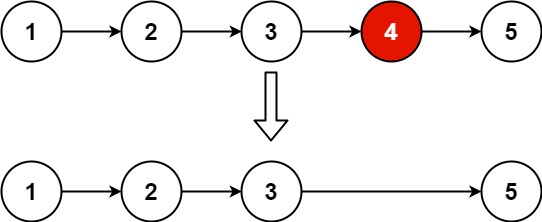
Follow up: Could you do this in one pass?
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
def remove_nth_from_end(head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
first = second = dummy
for i in range(n + 1):
first = first.next
while first:
first = first.next
second = second.next
second.next = second.next.next
return dummy.next
node1 = ListNode(1)
node2 = ListNode(2)
node3 = ListNode(3)
node4 = ListNode(4)
node5 = ListNode(5)
node1.next = node2
node2.next = node3
node3.next = node4
node4.next = node5
assert remove_nth_from_end(node1, 2) == [1,2,3,5], "Test case 1 failed"
node1 = ListNode(1)
assert remove_nth_from_end(node1, 1) == [], "Test case 2 failed"
node1 = ListNode(1)
node2 = ListNode(2)
node1.next = node2
assert remove_nth_from_end(node1, 1) == [1], "Test case 3 failed"