Array / String
A couple of “techniques” that are neither data structures nor algorithms but are commonly used in solving all kinds of problems are “Two-Pointer” (TP) and “Sliding Window” (SW).
These are not data structures because they don’t store data, and they are not algorithms because they don’t solve a specific problem. They are more like strategies that can be used to solve a wide variety of problems and are common enough to warrant its own LeetCode tags (TP tag and SW tag) and articles (TP article and SW article).
Two Pointer Technique
The two pointer technique is a simple and effective algorithmic technique that is used to solve problems involving arrays or linked lists. It involves using two pointers that move through the data structure at different speeds or in different directions to solve the problem.
Problems
-
Question 1. Valid Palindrome
Easy
A phrase is a palindrome if, after converting all uppercase letters into lowercase letters and removing all non-alphanumeric characters, it reads the same forward and backward. Alphanumeric characters include letters and numbers.
Given a string
s, returntrueif it is a palindrome, orfalseotherwise.def is_palindrome(s: str) -> bool: pass assert is_palindrome("A man, a plan, a canal: Panama") == True, "Test case 1 failed" assert is_palindrome("race a car") == False, "Test case 2 failed" assert is_palindrome("0P") == False, "Test case 3 failed" assert is_palindrome("ab_a") == True, "Test case 4 failed" assert is_palindrome(" ") == True, "Test case 5 failed" -
Question 2. Two Sum II - Input Array Is Sorted
Medium
Given a 1-indexed array of integers numbers that is already sorted in non-decreasing order, find two numbers such that they add up to a specific target number. Let these two numbers be numbers[index1] and numbers[index2] where 1 <= index1 < index2 <= numbers.length.
Return the indices of the two numbers, index1 and index2, added by one as an integer array [index1, index2] of length 2.
The tests are generated such that there is exactly one solution. You may not use the same element twice.
Your solution must use only constant extra space.
def two_sum(numbers: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
pass
assert two_sum([2,7,11,15], 9) == [1,2], "Test case 1 failed"
assert two_sum([2,3,4], 6) == [1,3], "Test case 2 failed"
assert two_sum([-1,0], -1) == [1,2], "Test case 3 failed"
-
Question 3. 3Sum
Easy
Given an integer array nums, return all the triplets
[nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]]such thati != j,i != k, andj != k, andnums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0.Notice that the solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
def three_sum(nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]: pass assert three_sum([-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]) == [[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]], "Test case 1 failed" assert three_sum([]) == [], "Test case 2 failed" assert three_sum([0]) == [], "Test case 3 failed" assert three_sum([0,1,1]) == [], "Test case 4 failed" assert three_sum([0,0,0]) == [[0,0,0]], "Test case 5 failed" -
Question 4. Container With Most Water
Medium
You are given an integer array height of length n. There are n vertical lines drawn such that the two endpoints of the ith line are (i, 0) and (i, height[i]).
Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container, such that the container contains the most water.
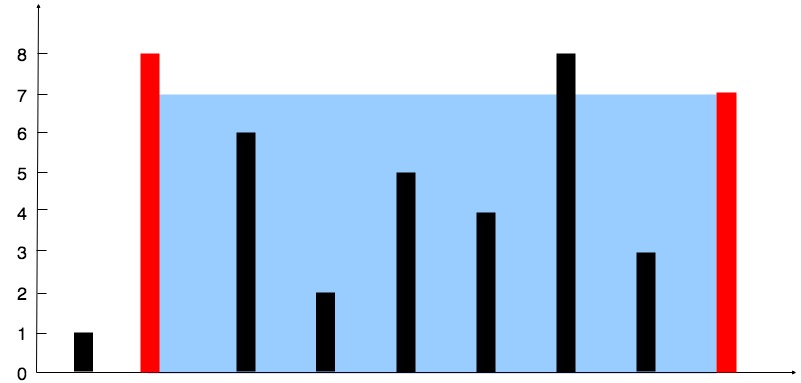
Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
def max_area(height: List[int]) -> int:
pass
assert max_area([1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]) == 49, "Test case 1 failed"
assert max_area([1,1]) == 1, "Test case 2 failed"
assert max_area([4,3,2,1,4]) == 16, "Test case 3 failed"
assert max_area([1,2,1]) == 2, "Test case 4 failed"
Sliding Window Technique
The sliding window technique is a common algorithmic technique used to solve problems involving arrays or strings. It involves maintaining a window of elements in the array or string and sliding the window across the data structure to find a solution.
-
Fixed Size Window: The window size is fixed, and the window slides one element at a time.
-
Variable Size Window: The window size can vary, and the window slides one element at a time.
-
Two Pointers: Two pointers are used to maintain the window boundaries.
Problems
-
Question 1. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
Easy
You are given an array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
You want to maximize your profit by choosing a single day to buy one stock and choosing a different day in the future to sell that stock.
Return the maximum profit you can achieve from this transaction. If you cannot achieve any profit, return 0.
def max_profit(prices: List[int]) -> int: pass assert max_profit([7,1,5,3,6,4]) == 5, "Test case 1 failed" assert max_profit([7,6,4,3,1]) == 0, "Test case 2 failed" assert max_profit([1,2]) == 1, "Test case 3 failed" assert max_profit([2,4,1]) == 2, "Test case 4 failed" -
Question 2. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
Medium
Given a string
s, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.For example,
Input:
"abcabcbb"
Output:3
Explanation: The answer is"abc", with the length of3.def length_of_longest_substring(s: str) -> int: pass assert length_of_longest_substring("abcabcbb") == 3, "Test case 1 failed" assert length_of_longest_substring("bbbbb") == 1, "Test case 2 failed" assert length_of_longest_substring("pwwkew") == 3, "Test case 3 failed" assert length_of_longest_substring("") == 0, "Test case 4 failed" -
Question 3. Longest Repeating Character Replacement
Medium
You are given a string
sand an integerk. You can choose any character of the string and change it to any other uppercase English character. You can perform this operation at mostktimes.Return the length of the longest substring containing the same letter you can get after performing the above operations.
def character_replacement(s: str, k: int) -> int: pass assert character_replacement("ABAB", 2) == 4, "Test case 1 failed" assert character_replacement("AABABBA", 1) == 4, "Test case 2 failed" assert character_replacement("A", 0) == 1, "Test case 3 failed" assert character_replacement("ABBB", 2) == 4, "Test case 4 failed" print("All test cases passed!")