Tree Problems
Problems
Question 1. Invert Binary Tree
Easy
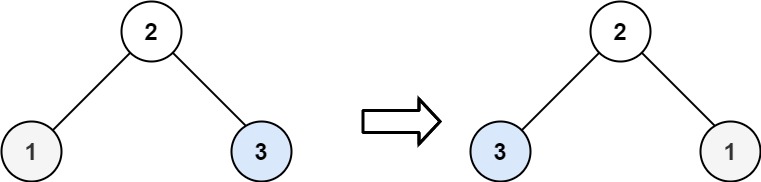
Given the root of a binary tree, invert the tree, and return its root.
Example 1 Input: [4,2,7,1,3,6,9] Output: [4,7,2,9,6,3,1]

Example 2 Input: [2,1,3] Output: [2,3,1]
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
def invert_tree(root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
pass
assert invert_tree([4,2,7,1,3,6,9]) == [4,7,2,9,6,3,1], "Test case 1 failed"
assert invert_tree([2,1,3]) == [2,3,1], "Test case 2 failed"
assert invert_tree([]) == [], "Test case 3 failed"
print("Test cases passed :)")
Question 2. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Easy
Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Example 1 Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 3

class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
def max_depth(root: TreeNode) -> int:
pass
assert max_depth([3,9,20,None,None,15,7]) == 3, "Test case 1 failed"
print("Test cases passed :)")
Question 3. Same Tree
Easy
Given the roots of two binary trees p and q, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical, and the nodes have the same value.
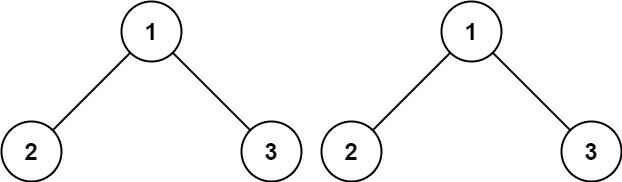
Example 1 Input: p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3] Output: True
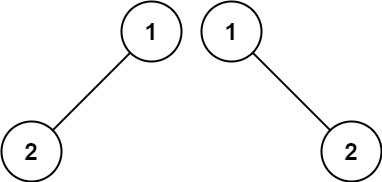
Example 2 Input: p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2] Output: False
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
def is_same_tree(p: TreeNode, q: TreeNode) -> bool:
pass
assert is_same_tree([1,2,3], [1,2,3]) == True, "Test case 1 failed"
assert is_same_tree([1,2], [1,None,2]) == False, "Test case 2 failed"
print("Test cases passed :)")
Question 4. Subtree of Another Tree
Easy
Given the roots of two binary trees root and subRoot, return true if there is a subtree of root with the same structure and node values of subRoot and false otherwise.
A subtree of a binary tree tree is a tree that consists of a node in tree and all of this node’s descendants. The tree tree could also be considered as a subtree of itself.
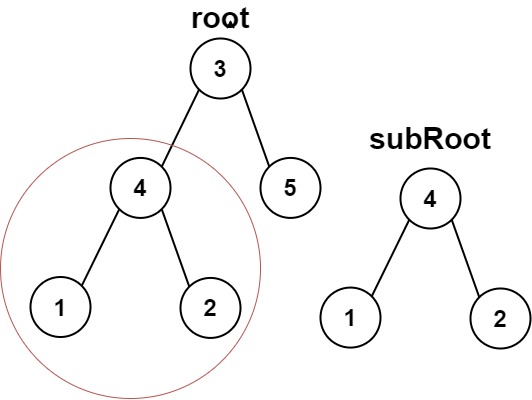
Example 1 Input: root = [3,4,5,1,2], subRoot = [4,1,2] Output: true
Example 2 Input: root = [3,4,5,1,2,null,null,null,null,0], subRoot = [4,1,2] Output: false
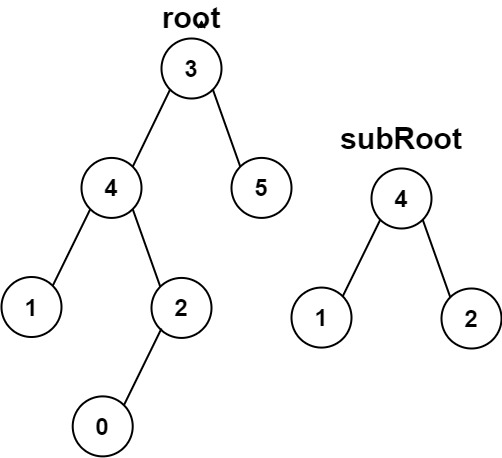
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
def is_subtree(root: TreeNode, subRoot: TreeNode) -> bool:
pass
assert is_subtree([3,4,5,1,2], [4,1,2]) == True, "Test case 1 failed"
assert is_subtree([3,4,5,1,2,None,None,None,None,0], [4,1,2]) == False, "Test case 2 failed"
print("Test cases passed :)")
Question 5. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
Medium
Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the BST.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Example 1 Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8 Output: 6
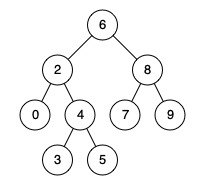
Example 2 Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4 Output: 2

class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
def lowest_common_ancestor(root: TreeNode, p: int, q: int) -> TreeNode:
pass
assert lowest_common_ancestor([6,2,8,0,4,7,9,None,None,3,5], 2, 8) == 6, "Test case 1 failed"
assert lowest_common_ancestor([6,2,8,0,4,7,9,None,None,3,5], 2, 4) == 2, "Test case 2 failed"
print("Test cases passed :)")
Question 6. Count Good Nodes in Binary Tree
Medium
Given a binary tree, return the number of good nodes in the tree.
A node node is a good node if in the path from root to that node, there are no nodes with a value greater than node.val.
Example 1 Input: root = [3,1,4,3,null,1,5] Output: 4
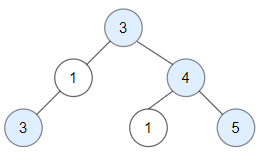
Example 2 Input: root = [3,3,null,4,2] Output: 3
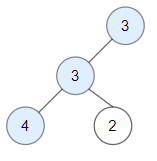
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
def good_nodes(root: TreeNode) -> int:
pass
assert good_nodes([3,1,4,3,None,1,5]) == 4, "Test case 1 failed"
assert good_nodes([3,3,None,4,2]) == 3, "Test case 2 failed"
print("Test cases passed :)")
Question 7. Validate Binary Search Tree
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree, determine if it is a valid binary search tree (BST).
A valid BST is defined as follows:
-
The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node’s key.
-
The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
-
Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1 Input: root = [2,1,3] Output: true

Example 2 Input: root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6] Output: false

class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
def is_valid_bst(root: TreeNode) -> bool:
pass
assert is_valid_bst([2,1,3]) == True, "Test case 1 failed"
assert is_valid_bst([5,1,4,None,None,3,6]) == False, "Test case 2 failed"
print("Test cases passed :)")