HashMaps
Hashing & Sets
Hashing is a technique used in data structures to store and retrieve data efficiently. It involves using a hash function to map data items to a fixed-size array which is called a hash table. Hash tables are used in a wide variety of applications, including databases, caching systems, and symbol tables.
Hash sets are collections of distinct elements that are stored in a way that allows for quick access and retrieval. Sets are commonly used in computer science to store unique elements and perform set operations such as union, intersection, and difference.
Sets are collections of distinct elements that are stored in a way that allows for quick access and retrieval. Sets are commonly used in computer science to store unique elements and perform set operations such as union, intersection, and difference.
- TOC {:toc}
Hash Table
Hash Table (also known as a hash map) is a fundamental data structure that efficiently stores and retrieves data in a way that allows for quick access. It involves mapping data to a specific index in a hash table using a hash function that enables fast retrieval of information based on its key. This method is commonly used in databases, caching systems, and various programming applications to optimize search and retrieval operations.
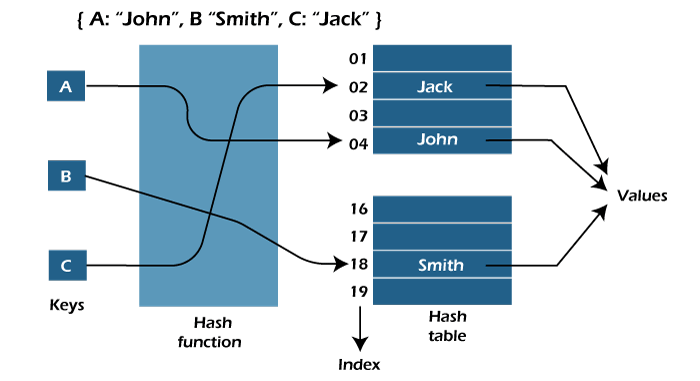

Hash Table in Python
In Python, hash tables are implemented using the dict data structure, which is a built-in data type that stores key-value pairs. Hash tables in Python are optimized for fast search, insert, and delete operations.
# Create a hash table
hash_table = {}
# Insert a key-value pair
hash_table["key1"] = "value1"
# Retrieve a value based on key
value = hash_table["key1"]
# Check if a key is in the hash table
if "key1" in hash_table:
print("Key found in hash table")Hash Table Operations
Hash tables support a variety of operations, including:
- Search: Retrieve the value associated with a key.
- Insert: Add a new key-value pair to the hash table.
- Delete: Remove a key-value pair from the hash table.
- Update: Change the value associated with a key.
- Size: Get the number of key-value pairs in the hash table.
# Create a hash table
hash_table = {}
# Insert key-value pairs
hash_table["key1"] = "value1"
hash_table["key2"] = "value2"
hash_table["key3"] = "value3"
# Search for a key
value = hash_table.get("key2")
# Delete a key
del hash_table["key3"]
# Update a value
hash_table["key1"] = "new_value"
# Get the size of the hash table
size = len(hash_table)Time and Space Complexity
The time complexity of hash table operations depends on the efficiency of the hash function and the collision resolution technique. In general, hash table operations have an average-case time complexity of O(1) for search, insert, and delete operations.
The space complexity of a hash table is O(n), where n is the number of key-value pairs stored in the table. The space complexity can vary based on the load factor and the collision resolution technique used.